AP-BM Asphalt plant
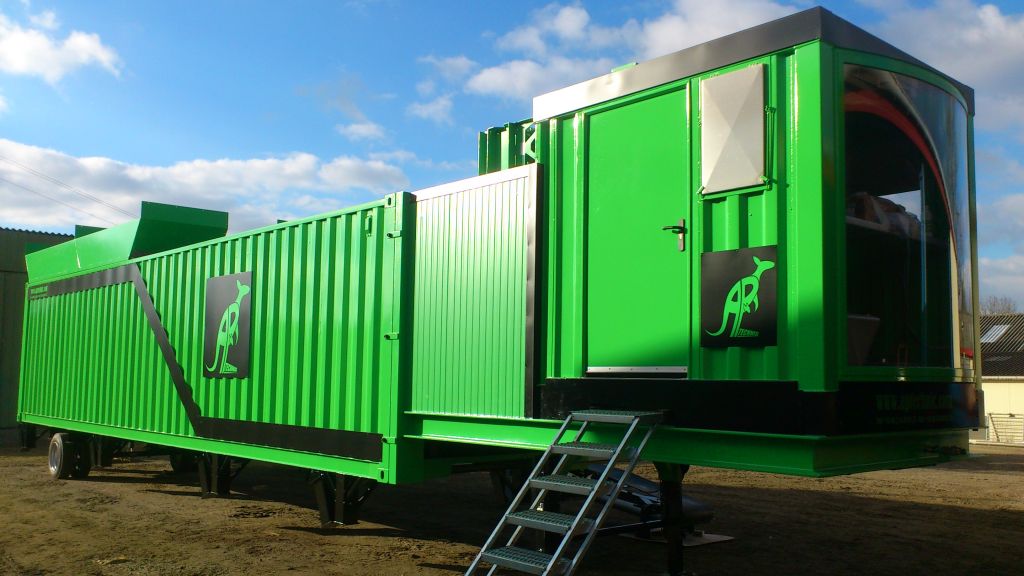

AP-BM Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-BM model is a c ontinuous, parallel-flow mobile plant , containerized for harsh climatic conditions, consisting of two trailers. 1 trailer with four feeders , a d ...
Read more
AP-BM Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-BM model is a c ontinuous, parallel-flow mobile plant , containerized for harsh climatic conditions, consisting of two trailers. 1 trailer with four feeders , a d ...
Read more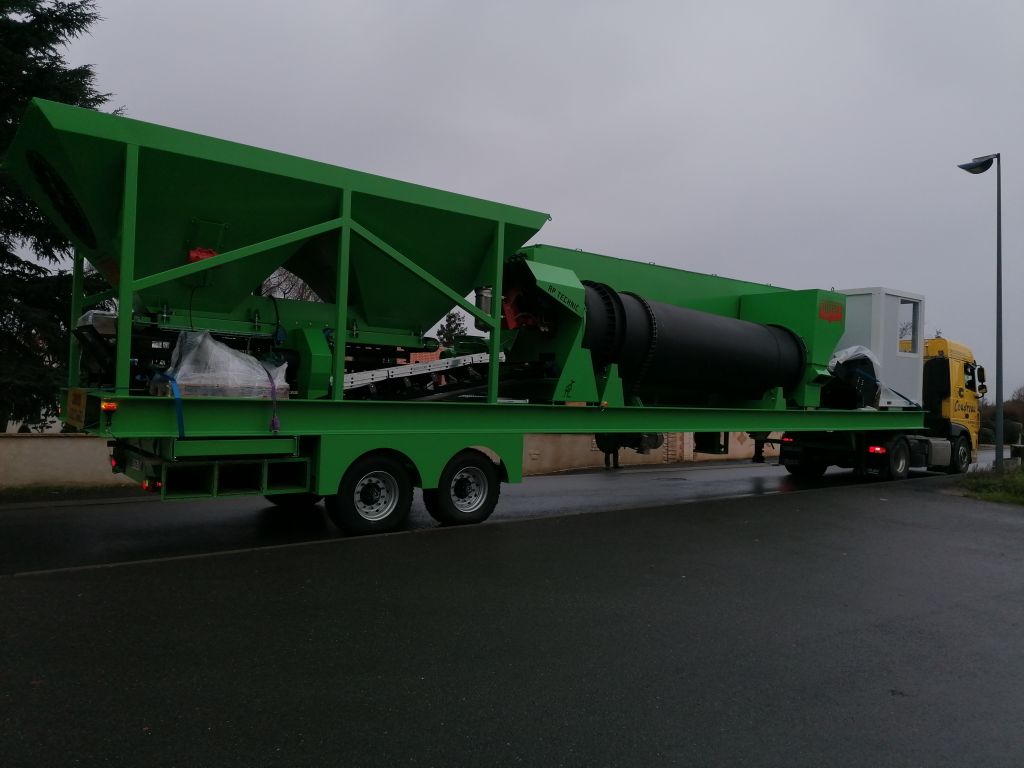
AP-BMS Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-BMS model is a compact, continuous, mobile, parallel-flow mixing hot asphalt plant consisting of one trailer. Trailer comprising: - 4 feeders - 1 complete baghou ...
Read more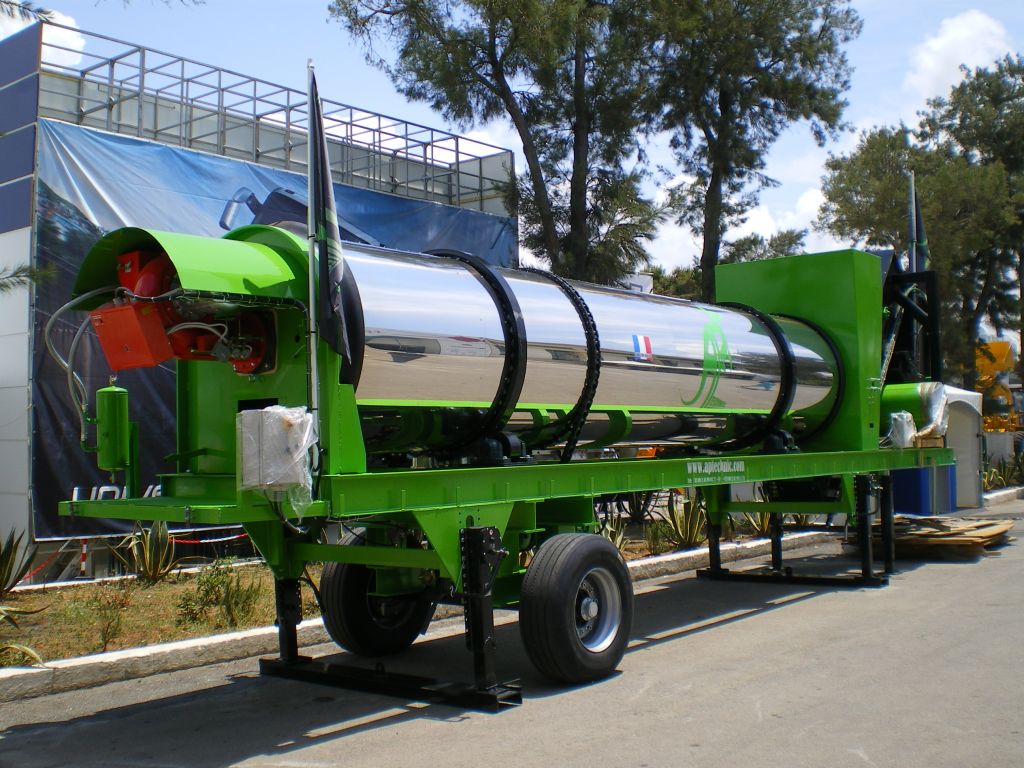
AP-BS Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-BS model is a continuous, parallel-flow mobile mixing hot asphalt plant consisting of two to three trailers. 1 trailer with four feeders 1 baghouse filter trailer ...
Read more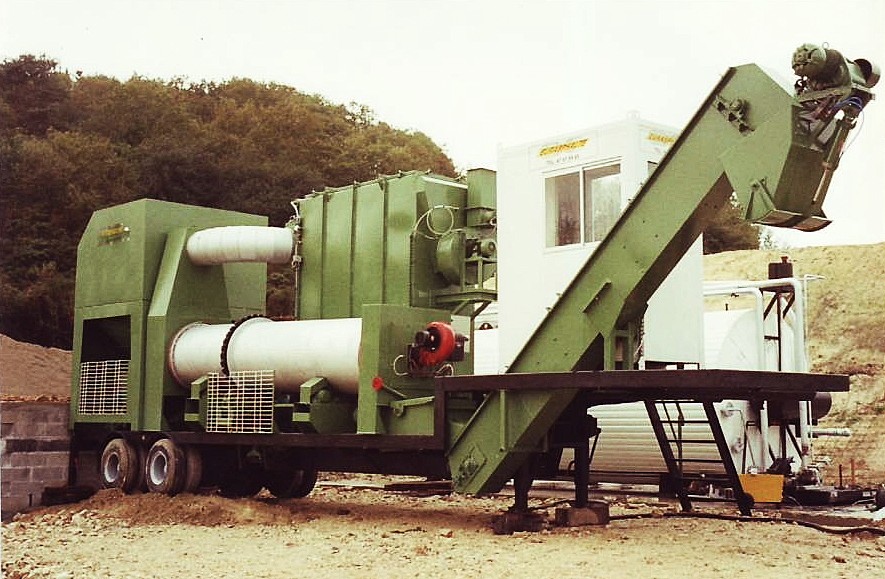
AP-M Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-M model is a small continuous mixing hot asphalt plant, available in parallel or counter-flow versions, consisting of one trailer. 1 trailer comprising pre-batcher ...
Read more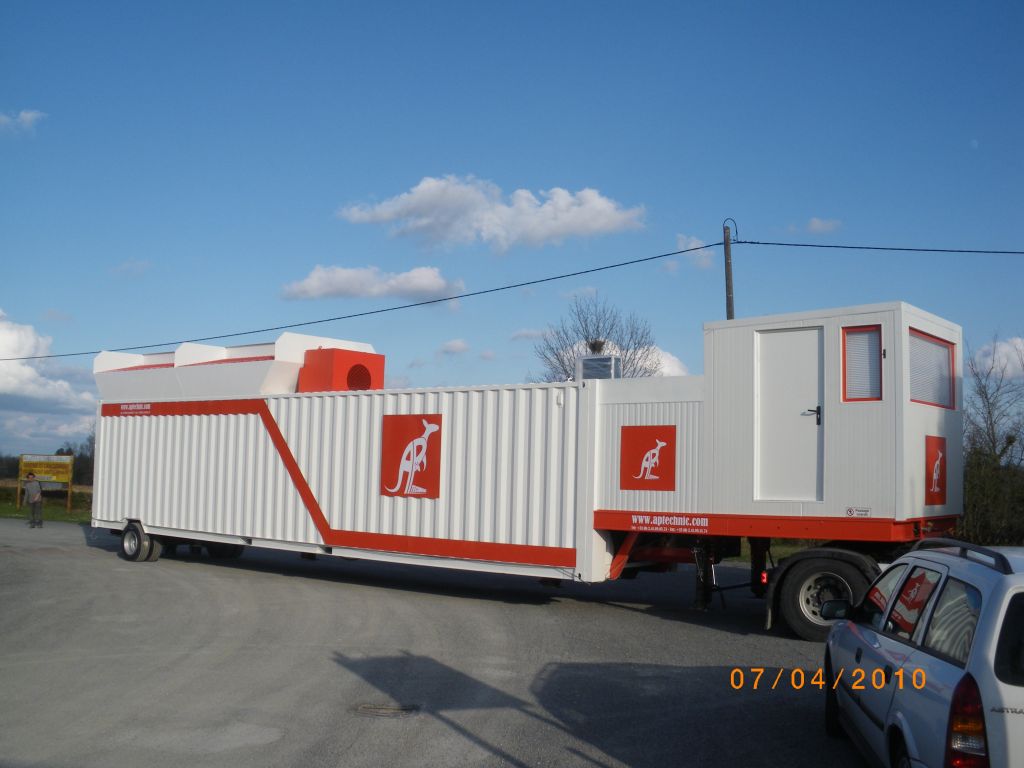
AP-RM Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-RM model is a containerized mobile continuous hot asphalt plant for harsh weather conditions. It operates in a counterflow mode and can produce colored asphalt mi ...
Read more
AP-RS Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-RS mode l is a continuous, counter-flow mobile hot asphalt plant capable of producing asphalt mixes with additives, colored asphalt, hot or cold asphalt , and can ...
Read more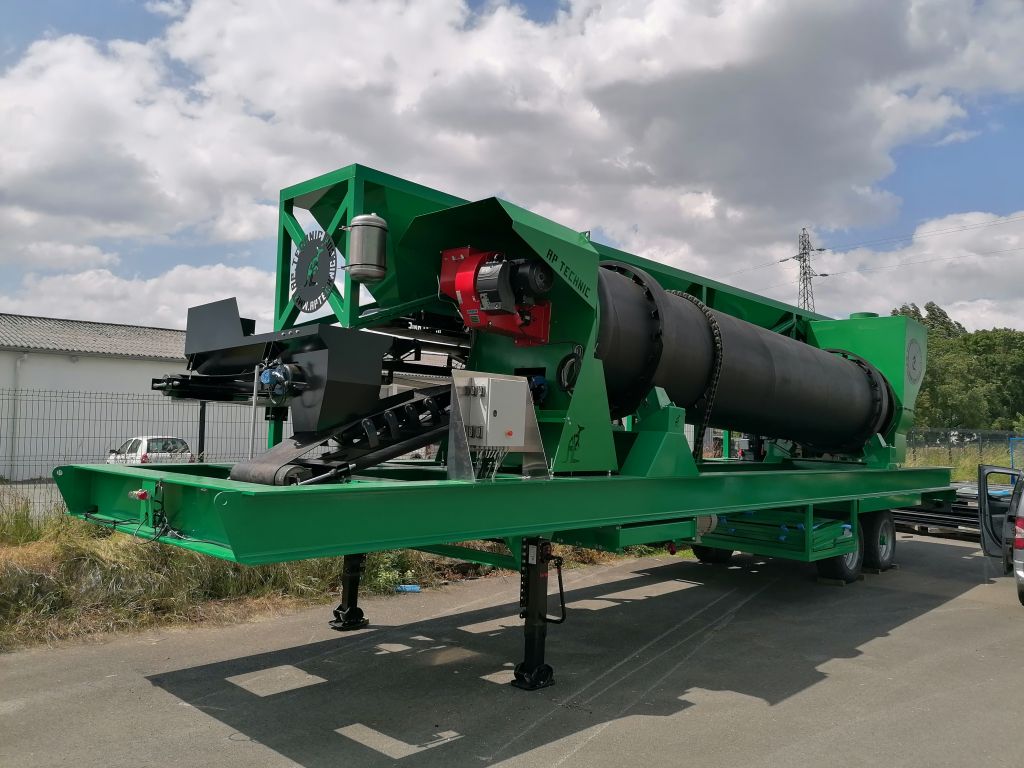
AP-SBM 2 R Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-SBM 2 R is a hyper-mobile continuous mixing hot asphalt plant available in two versions: counterflow or parallel flow, mounted on two trailers. This plant of ...
Read more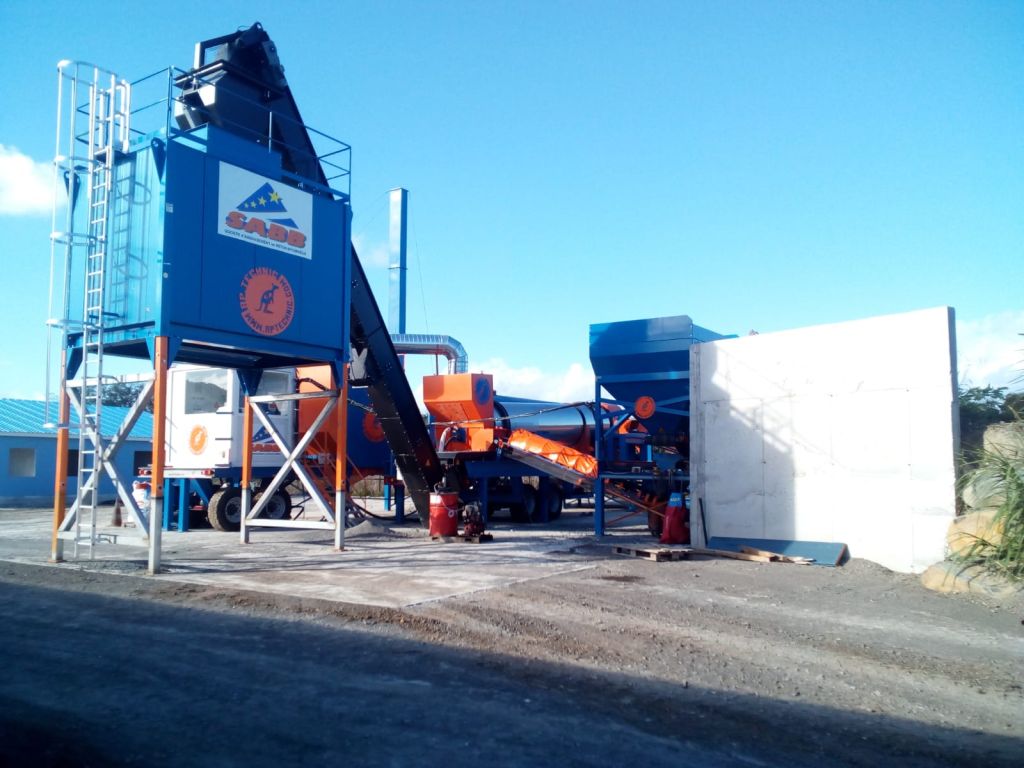
AP-SBM 3 R Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-SBM 3 R model is a hyper-mobile , continuous, parallel-flow hot and cold asphalt plant mounted on three trailers. This plant offers the advantage of being su ...
Read more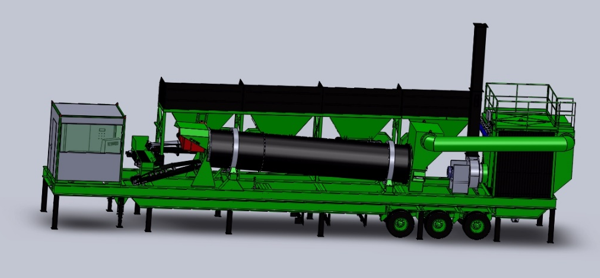
AP-SBM Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-SBM model is a hyper-mobile, continuous, parallel-flow mixing asphalt plant mounted on a single trailer. This plant offers the advantage of being suitable for mo ...
Read more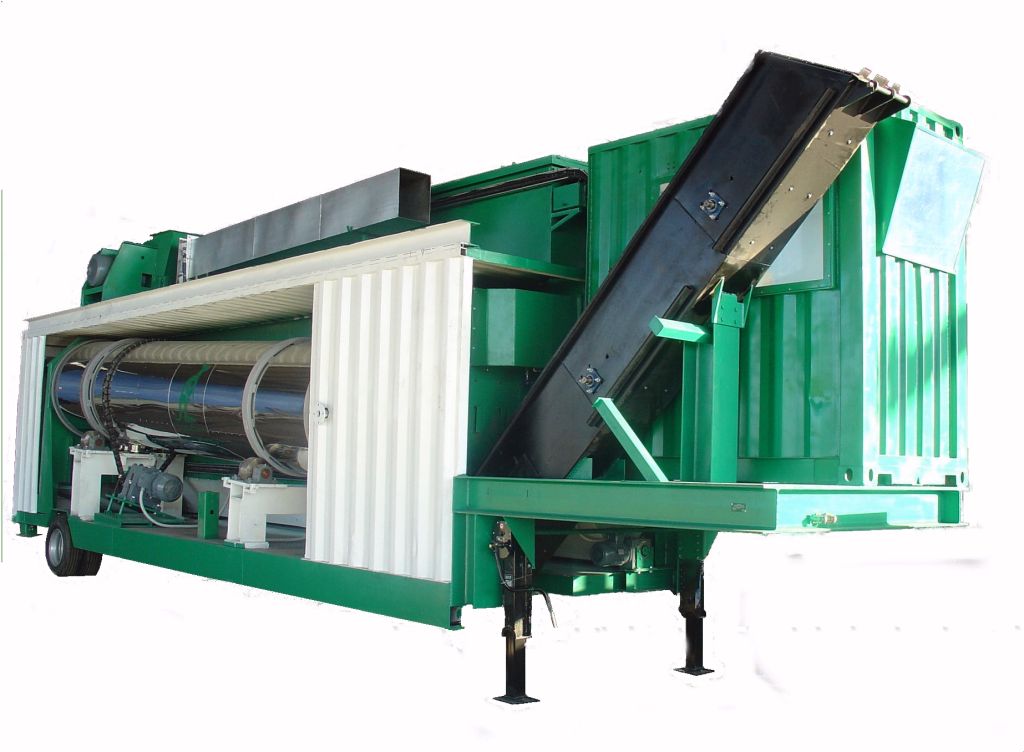
AP-TM Asphalt Mixing Plant The AP-TM model is an ultra-compact, continuous, parallel-flow mobile hot asphalt plant , mounted on one or two containerized trailer s depending on the desired configur ...
Read moreA bitumen mixing plant, also known as an asphalt plant, is an industrial facility used for the production of bituminous mix. This material is obtained by mixing aggregates (such as gravel, sand, and fillers) with a hydrocarbon binder, usually bitumen. The asphalt produced is mainly used for the construction and renovation of pavements, roads, parking lots, and runways.
How does an asphalt plant work?
The process of producing asphalt includes several key steps:
There are mainly two types of asphalt plants:
The coating of aggregates with a binder, primarily bitumen, has the main objectives:
A.P. Technic 27 rue du moulin de groleau 49490 Noyant-Villages - FRANCE Tél. +33 (0) 241 890 373 Contact us